Robotics in Food and beverage Industry
Our lives depend on the food and beverage industry and it is in a constant state of evolution, affected by shifting consumer demands and new technologies. Particularly noteworthy is the industry's adaptation to cope with labor shortages and the surge in online business inquiries, both of which have been amplified by the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic. In response, food and beverage manufacturers are increasingly turning to automation and robotics to accelerate operations, increase efficiency, and meet the growing demands of consumers, both online and offline. In what is coming next we will discover why the food and beverage industry needs robots and what is next for those robots.
Challenges in the Food and Beverage Industry

Labor Shortages
Labor shortages have become a significant challenge for industries, worsened by factors like rising demand and the labor-intensive nature of eCommerce operations. To address these challenges, businesses are increasingly implementing automation solutions to cope with limitations in the workforce.
Integration of Automation
The integration of automation has revolutionized industry dynamics, offering solutions to mitigate labor shortages and enhance operational efficiency. However, challenges persist in implementing and standardizing automation solutions across various production processes, necessitating a careful balance between human and automated workforces.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements, including AI, computer vision, and gripper technology, have played a pivotal role in addressing industry challenges. Yet, the rapid pace of technological change presents its own set of challenges, requiring companies to adapt and innovate continually to remain competitive.
Sanitation and Hygiene
Maintaining sanitation and hygiene standards remains paramount in food and beverage manufacturing, particularly amidst increased automation. Innovations in sanitary design for robotic equipment have emerged to address concerns of contamination and ensure food safety throughout the production process.
Resource Constraints for SMEs
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) face unique challenges in adopting automation solutions, including resource limitations and lack of technical expertise. Overcoming these barriers requires accessible and affordable automation options tailored to the needs of SMEs.
Market Dynamics and Competition
Evolving market dynamics and competitive pressures drive the adoption of automation in the food and beverage industry. Meeting consumer expectations for freshness and quality while navigating labor shortages necessitates agility and innovation to remain competitive.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance poses significant challenges for industry stakeholders, particularly in automated processes. Adhering to regulatory standards and guidelines requires collaboration with regulatory authorities and meticulous attention to detail.
Cost and ROI Considerations
Assessing the cost-benefit of automation solutions is crucial for industry stakeholders, balancing initial investment costs with long-term savings. Calculating return on investment (ROI) and overcoming financial constraints are essential considerations in the adoption of automation.
Training and Skill Development
Transitioning to automated workforces necessitates training and skill development initiatives to upskill employees for new roles. Overcoming resistance to change and investing in continuous learning programs are critical for a smooth transition to automated processes.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions pose significant challenges to industry operations, requiring resilience and flexibility in supply chain management. Strategies for mitigating risks and enhancing supply chain efficiency are essential to navigate these challenges effectively.
Applications of Robotics in Food Manufacturing
In recent years, the integration of robotics has transformed the landscape of food manufacturing, offering unprecedented levels of efficiency, precision, and safety. In this blog we talk about the diverse applications of robotics in the food manufacturing industry, highlighting the ways in which automation is revolutionizing production processes.
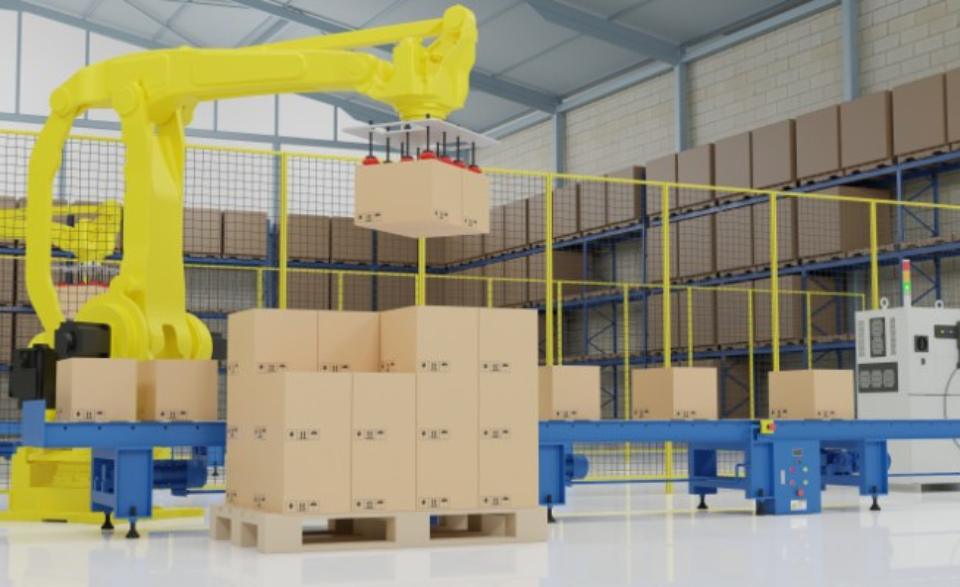

Food Processing and Packaging
Robotics play a pivotal role in food processing, from automated milking of cows to cutting meats and slicing fruits and vegetables. These processes, once labor-intensive and time-consuming, are now streamlined and optimized through the use of robotic arms and automation technologies. Additionally, robots are essential in packaging food products, ensuring accuracy and consistency in packaging processes.
Food Sanitation
The importance of sanitation in food manufacturing cannot be overstated, and robotics are instrumental in enhancing hygiene standards. Automated production and processing lines minimize human contact with food products, reducing the risk of contamination. Furthermore, robotic equipment can be quickly cleaned and sterilized to a high standard, ensuring compliance with stringent food safety regulations.
Food Delivery
The latest development in the application of robotics in the food industry is in the realm of food delivery. Technology and automation have enabled the deployment of automated, self-guiding food delivery robots in various locations, providing a solution to the growing demand for convenient and efficient food delivery services.
Types of Robots Used:
Articulated Robots:
Mimic the movements of human arms and are used for various tasks, including food processing and packaging.
Cartesian Robots:
Operate on three axes, allowing for vertical and horizontal movement in food manufacturing processes.
SCARA Robots:
Ideal for fixed-position tasks, such as picking and placing items in food packaging operations.
Delta Robots:
Comprising three robotic arms working in tandem, often used for picking and placing roles in food manufacturing.
The applications of robotics in food manufacturing are vast and varied, encompassing everything from food processing and packaging to sanitation and delivery. As technology continues to advance, the role of robotics in the food industry will only continue to expand, driving efficiency, innovation, and safety across the production process. By embracing automation, food manufacturers can stay ahead of the curve and meet the evolving needs of consumers in a rapidly changing market landscape.
Benefits of Robots in the Food Industry
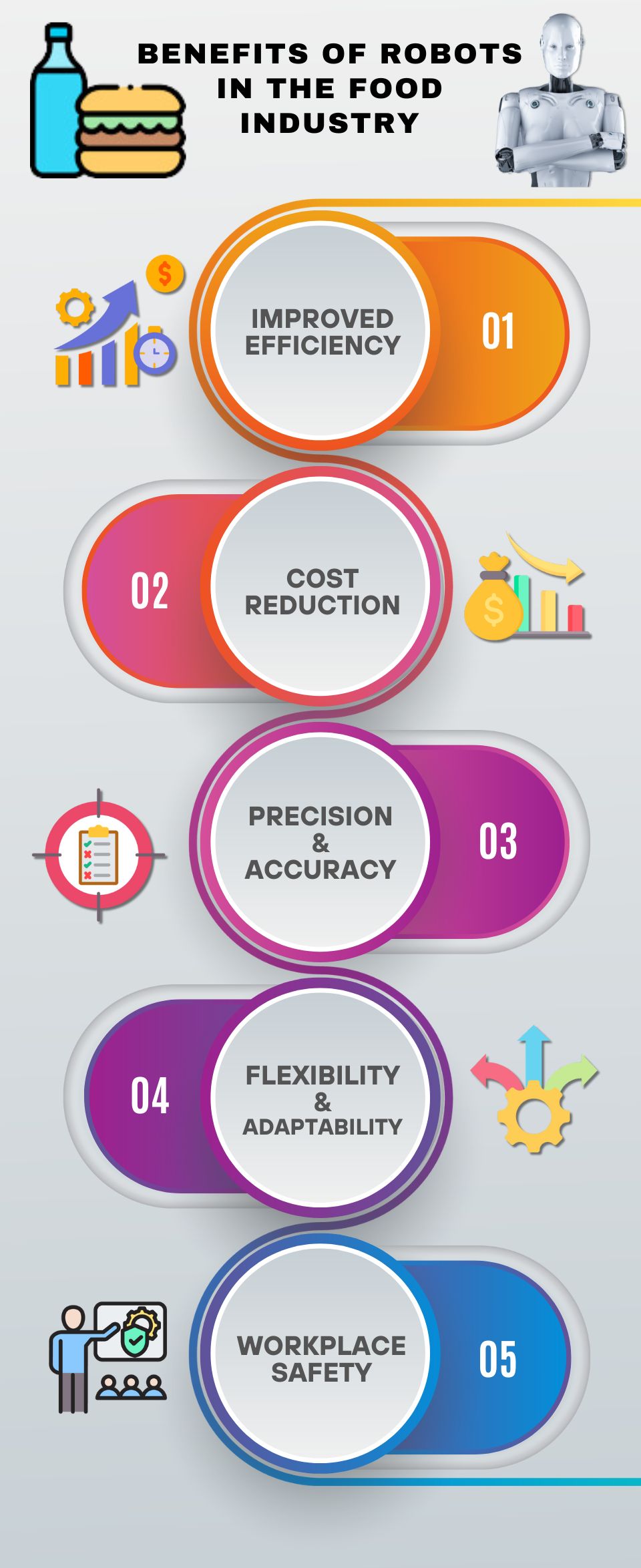
In our tech-driven world, robots are vital in the food industry. They're changing how things are made, making processes better, safer, and higher quality. In this part, we'll explore why using robots in food production is such a game-changer, showing how automation is revolutionizing the industry.
Improved Efficiency
- Robots simplify production processes, executing tasks with speed and precision.
- Automated workflows reduce cycle times and increase output, leading to higher productivity and resource utilization.
- labor-intensive and time-consuming tasks are now completed swiftly and consistently, resulting in operational efficiency.
Enhanced Food Safety and Hygiene
- Automation minimizes human contact with food products, reducing the risk of contamination and ensuring compliance with stringent food safety regulations.
- Robotic equipment can be cleaned and sterilized easily, ensuring high hygiene standards during production.
- High-tech sensors and monitoring systems find and prevent risks, keeping food products safe and top quality
Cost Reduction
- By automating repetitive tasks, robots reduce labor costs and overhead expenses associated with manual labor.
- Increased efficiency and productivity lead to lower operational costs and higher profitability for food manufacturers.
- Long-term cost savings are realized through reduced waste, improved resource utilization, and optimized production processes.
Precision and Accuracy
- Robots perform tasks with a high degree of accuracy and consistency, minimizing errors and product defects.
- Precision in food processing and packaging ensures uniformity and quality across batches, enhancing consumer satisfaction and brand reputation.
- Advanced robotics technologies, such as computer vision and machine learning, enable precise handling of diverse food products and packaging formats.
Flexibility and Adaptability
- Robotics offer versatility in handling a wide range of food products, from delicate fruits and vegetables to heavy-duty packaging materials.
- Automated systems can be easily reconfigured and programmed to adapt to changing production requirements and market demands.
- Flexibility in production processes allows food manufacturers to respond quickly to fluctuations in demand and product variations.
Workplace Safety
- Automation reduces the risk of workplace injuries and occupational hazards associated with manual labor.
- Robots handle tasks that are repetitive, strenuous, or hazardous for human workers, ensuring a safer work environment.
- Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human operators, providing assistance and support while adhering to strict safety protocols.
Future Trends of Robots in the Food and Beverage Industry
As the food and beverage industry continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences, the role of robots in manufacturing processes is set for significant expansion. In this section, we talk about the future trends and innovations shaping the landscape of robotics in the food and beverage industry, offering insights into the transformative potential of automation.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
- AI-powered robots are revolutionizing food manufacturing processes, enabling predictive maintenance, quality control, and adaptive production strategies.
- Machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets to optimize production parameters, enhance product quality, and minimize waste.
- Autonomous decision-making capabilities empower robots to adapt to dynamic production environments, driving efficiency and agility.
Collaborative Robotics (Cobots):
- The adoption of collaborative robots is on the rise, as manufacturers seek to augment human capabilities and improve workplace safety.
- Cobots work alongside human operators, facilitating human-robot collaboration in tasks that require dexterity, flexibility, and precision.
- Enhanced safety features and intuitive interfaces make cobots ideal for small-batch production, customization, and rapid changeovers.
Vision-Guided Robotics:
- Vision-guided robots leverage advanced imaging technologies to navigate complex environments, detect objects, and perform intricate tasks.
- High-resolution cameras and 3D vision systems enable robots to identify and manipulate food products with unmatched accuracy and efficiency.
- Applications include pick-and-place operations, quality inspection, and sorting tasks, enhancing productivity and quality assurance.
Modular and Scalable Automation Solutions:
- Modular automation platforms enable food manufacturers to customize and scale robotic systems according to their specific production needs.
- Plug-and-play components and standardized interfaces facilitate seamless integration with existing equipment and production lines.
- Scalable solutions accommodate fluctuations in demand, allowing manufacturers to optimize resource utilization and adapt to market dynamics.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Connectivity:
- IoT-enabled robotics systems create interconnected ecosystems, facilitating real-time monitoring, data analytics, and remote management.
- Sensors embedded in robots and production equipment gather valuable performance data, enabling predictive maintenance and process optimization.
- Connectivity with cloud-based platforms and enterprise systems enhances visibility, transparency, and traceability across the supply chain.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Robotics:
- The future of robotics in the food industry emphasizes sustainability and environmental responsibility, with a focus on energy efficiency and waste reduction.
- Green robotics solutions incorporate renewable energy sources, recyclable materials, and eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
- Robotics technologies support sustainable agriculture practices, resource conservation, and circular economy initiatives, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Finishing bites
Thank you for joining us on this insightful journey through the transformative landscape of the food industry. From exploring the applications of robotics to uncovering future trends and innovations, we've witnessed the profound impact of technology and innovation on shaping the future of food. As we continue to embrace change and adapt to new challenges, let's remain inspired by the endless possibilities that lie ahead. Together, let's forge a path towards a more sustainable, efficient, and consumer-centric food ecosystem. Here's to a future filled with innovation, collaboration, and delicious possibilities. Cheers to the future of food!
Keep the conversation going! Check out this related post.
Recent Posts
-
Booster Pump Troubleshooting and Maintenance: How to Fix and Prevent Common Issues
1. Introduction Imagine turning on your faucet only to be greeted with a weak trickle of water when …22nd Apr 2025 -
Energy-Efficient Booster Pumps: Selection and Tips for Maximizing Performance
1. Introduction Imagine never having to deal with fluctuating water pressure, noisy pumps, or skyroc …19th Apr 2025 -
Booster Pumps for Sustainable Water Systems: Irrigation and Rainwater Harvesting Solutions
1. Introduction Water scarcity is no longer a distant threat—it’s a reality affecti …16th Apr 2025




