Defending Against Risks: Pressure Sensor Safety Strategies You Should Consider Part 2
Navigating safety considerations around pressure sensors in hazardous environments involves a complex interplay of standards, regulations, and practical applications. Ensuring safety involves understanding the risks associated with these sensors, implementing proper installation, maintenance, and protective measures, and staying compliant with industry-specific standards. It's a multifaceted landscape that necessitates a comprehensive approach to mitigate potential hazards and create a secure working environment. If you have more specific inquiries or need detailed information, don't hesitate to ask!
In our previous blog, we talked about the safety tips and the issues that non-compliance with these tips creates for us. Also, in the first part, the certificates that a pressure sensor must have were mentioned. In this blog, attention has been paid to the safety points that should be observed in high-risk places and the pressure sensors that are used in hazardous environments.

Fig 1. Hazardous area
How are Proper wiring and grounding practices in hazardous locations?
Proper wiring and grounding practices in hazardous locations are critical for ensuring safety, preventing ignition sources, and maintaining electrical integrity. Here's how to implement these practices in hazardous environments:
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhere to local regulations and standards (such as NEC, IEC, ATEX, or NFPA) specific to hazardous areas. These regulations provide guidelines for wiring methods, equipment selection, and grounding practices.
- Cable and Conduit Selection: Use cables, conduits, and wiring systems designed for hazardous locations. Employ appropriate cable types, such as armored or shielded cables, capable of withstanding the environment and preventing damage that could expose wires to ignition sources.
- Intrinsically Safe Wiring Techniques: Implement intrinsically safe (IS) wiring techniques for hazardous areas where necessary. Use barriers, isolators, or other devices to limit electrical energy and prevent sparking or heat generation that could ignite a flammable atmosphere.
- Proper Installation and Segregation: Install wiring in a manner that prevents damage and maintains proper segregation between power and control circuits. Keep low-voltage and high-voltage wiring separated to minimize the risk of induction or interference.
- Explosion-Proof Enclosures: Utilize explosion-proof enclosures for wiring junctions or connections. These enclosures are designed to contain any potential explosion, preventing it from igniting the surrounding atmosphere.
- Grounding and Bonding: Ensure proper grounding and bonding of electrical equipment and metal structures in hazardous areas. Grounding helps dissipate static charges and prevents the buildup of potentially hazardous voltages. Bonding connects metal parts to prevent differences in potential that could lead to sparking.
- Equipment Selection: Choose equipment with proper grounding provisions and ensure the integrity of connections. Employ equipment specifically designed for hazardous locations and that includes grounding terminals or provisions.
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Conduct routine inspections to check the condition of wiring, connections, and grounding systems. Address any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections promptly to maintain electrical safety.
- Training and Awareness: Provide training to personnel working in hazardous areas on proper wiring practices, grounding procedures, and the importance of adhering to safety protocols.
Implementing these wiring and grounding practices ensures electrical safety, reduces the risk of ignition sources, and helps maintain a secure working environment in hazardous locations.
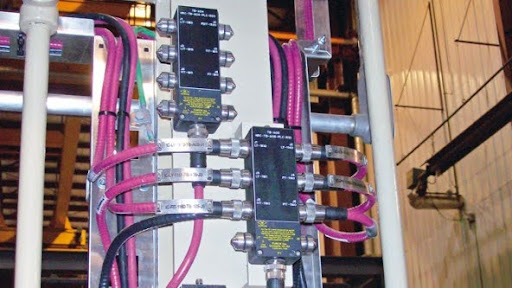
Fig 2. Proper wiring for hazardous place
Importance of regular maintenance and inspection of pressure transmitters in hazardous areas
Regular maintenance and inspection of pressure transmitters in hazardous areas are crucial for several reasons:
What are the proper maintenance pressure sensors in hazardous areas?
Proper maintenance of pressure sensors in hazardous areas is essential to ensure their reliability, accuracy, and safety. Here's a guideline for maintaining these sensors:
- Scheduled Inspections: Establish a regular inspection schedule based on manufacturer recommendations and industry standards. Inspect pressure sensors for signs of damage, corrosion, or wear. Check seals, connections, and housing integrity.
- Calibration Checks: Perform periodic calibration checks to verify the accuracy of pressure readings. Calibration ensures that the sensor provides precise measurements, especially in critical applications within hazardous areas.
- Cleaning and Protection: Keep sensors clean and free from contaminants. Use appropriate cleaning methods and materials compatible with the sensor's construction and the hazardous environment. Protect sensors from exposure to corrosive substances or harsh conditions that could degrade their performance.
- Environmental Monitoring: Monitor the environmental conditions in which pressure sensors operate. Regularly check for changes in temperature, pressure, or exposure to hazardous substances that could affect sensor performance.
- Documentation and Records: Maintain detailed records of maintenance activities, calibration results, and any observed issues. This documentation helps track sensor performance over time and facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Replacement of Components: Replace worn-out seals, gaskets, or other components as recommended by the manufacturer. Ensure that replacement parts are compatible and certified for use in hazardous areas.
- Training and Personnel Competence: Train personnel responsible for sensor maintenance on proper procedures, safety protocols, and handling techniques specific to hazardous areas. Ensure they understand the risks and safety measures required for maintenance activities.
- Emergency Procedures: Have clear and accessible emergency procedures in place for handling sensor malfunctions or emergencies in hazardous areas. Train personnel on these procedures to respond effectively to any incidents.
- Vendor Support and Guidelines: Engage with sensor manufacturers or vendors for guidance on best maintenance practices, specific to the model of pressure sensor being used in hazardous areas.
- Risk Assessment and Continuous Improvement: Conduct periodic risk assessments to identify potential issues or vulnerabilities in sensor operation within hazardous areas. Implement corrective actions and continuously improve maintenance practices based on findings.
By following these maintenance guidelines, industries can ensure the reliability, accuracy, and safety of pressure sensors operating in hazardous environments. Regular maintenance not only enhances the sensor's performance but also contributes to a safer working environment by minimizing the risks associated with potentially explosive atmospheres.
Compliance with periodic inspections and testing requirements
Periodic inspections and testing are crucial for ensuring equipment's ongoing reliability, safety, and compliance, especially in hazardous areas. Compliance with periodic inspections and testing requirements involves several key aspects:
- Regulatory and Standards Compliance: Understand the regulatory requirements and industry standards relevant to the equipment operating in hazardous areas. Regulations such as ATEX, IECEx, NEC, or specific industry guidelines often mandate periodic inspections and testing.
- Scheduled Inspection Plans: Develop and maintain a scheduled inspection plan based on manufacturer recommendations, regulatory requirements, and the criticality of the equipment. This plan outlines the frequency and scope of inspections and testing needed for compliance.
- Routine Inspections: Conduct routine inspections at specified intervals, checking for signs of wear, damage, or deterioration. Verify the integrity of components, electrical connections, enclosures, seals, and any safety features specific to hazardous environments.
- Functional Testing: Perform functional tests to ensure that the equipment operates as intended in hazardous areas. This may involve verifying pressure readings, temperature measurements, or other operational parameters to confirm accuracy and reliability.
- Calibration Checks: Periodically calibrate equipment, including pressure sensors, to ensure accurate measurements in hazardous environments. Calibration confirms that the equipment remains within specified tolerances and meets accuracy requirements.
- Documentation and Records: Maintain comprehensive records of inspections, tests, calibrations, and any corrective actions taken. These records serve as evidence of compliance, track equipment performance over time, and support regulatory audits or assessments.
- Qualified Personnel: Ensure that inspections and testing are conducted by qualified personnel trained in handling equipment in hazardous areas. Proper training ensures compliance with safety protocols and proficiency in performing inspections.
- Risk-Based Assessments: Consider risk-based assessments when determining the frequency and depth of inspections. Critical equipment or components may require more frequent and detailed inspections based on their impact on safety and operations.
- Adherence to Manufacturer Guidelines: Follow manufacturer guidelines and recommendations for inspections, testing intervals, and maintenance practices specific to the equipment used in hazardous environments.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously review and improve inspection and testing procedures based on findings, industry developments, or changes in regulations. Implement corrective measures to address identified issues and enhance equipment reliability and safety.
Compliance with periodic inspections and testing requirements is essential for maintaining equipment integrity, ensuring safety, and meeting regulatory standards in hazardous areas. It helps identify potential issues early, mitigates risks, and supports a safe working environment.
How can repair and replace a pressure sensor in hazardous environments according to safety guidelines?
Repairing or replacing a pressure sensor in hazardous environments requires strict adherence to safety guidelines to mitigate risks and ensure the safety of personnel and the environment. Here's a guideline for safely conducting repairs or replacements:
- Hazardous Area Assessment: Assess the hazardous area where the pressure sensor needs repair or replacement. Determine the classification (Zone 0, Zone 1, or Zone 2) and understand the specific risks associated with that area.
- Isolation and Lockout Procedures: Implement isolation procedures to shut down power and isolate the sensor from electrical sources. Use lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental energization during repair or replacement.
- Permit-to-Work System: Implement a permit-to-work system, ensuring that only authorized and trained personnel conduct repairs or replacements in hazardous areas. This system includes risk assessments, safety measures, and authorization before initiating work.
- Equipment De-Energization: Ensure that all power sources are turned off, and the equipment is de-energized before initiating any repair or replacement activities.
- Use of Intrinsically Safe Tools: Use intrinsically safe tools and equipment suitable for use in hazardous environments. Avoid tools that could generate sparks or heat.
- Proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Ensure personnel wear appropriate PPE, including flame-resistant clothing, safety goggles, gloves, and footwear designed for hazardous areas.
- Gas Testing and Ventilation: Conduct gas testing to ensure the absence of hazardous substances or gases before initiating repair or replacement. Provide adequate ventilation if needed.
- Handling and Transport: Handle the pressure sensor with care and follow proper handling procedures. Use suitable lifting or transport equipment to move the sensor safely without causing damage.
- Equipment Replacement: If replacing the sensor, ensure the new sensor is compatible, certified for use in the hazardous area, and properly installed following manufacturer guidelines.
- Testing and Verification: After repair or replacement, conduct tests to verify the proper functioning and accuracy of the pressure sensor. Calibrate the sensor if necessary to ensure accurate readings.
- Post-Work Cleanup: Dispose of any waste materials properly, clean the work area, and ensure no tools or debris are left behind. Follow waste disposal guidelines specific to hazardous materials.
- Documentation and Reporting: Maintain detailed records of the repair or replacement activities, including inspections, tests performed, any issues encountered, and corrective actions taken. Report any deviations or incidents as per company protocols.
Adhering to these safety guidelines helps minimize the risks associated with repairing or replacing pressure sensors in hazardous environments, ensuring a safer work environment and preventing potential accidents or hazards.

Fig 3. A proper pressure sensor for hazardous environment
What is the Personal Protective Equipment while using pressure sensors?
When working with pressure sensors, especially in hazardous environments, certain Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) helps ensure the safety of personnel. Here are essential PPE items:
- Safety Glasses/Goggles: Protect the eyes from flying debris, chemical splashes, or other hazards that may occur during the installation, maintenance, or repair of pressure sensors.
- Flame-Resistant Clothing: Wear clothing made of flame-resistant materials to reduce the risk of burns in case of fire or sparks in hazardous areas.
- Gloves: Use chemical-resistant or insulated gloves to protect hands from chemicals, sharp edges, or hot surfaces when handling pressure sensors or associated equipment.
- Safety Shoes/Boots: Wear safety footwear with steel toes and slip-resistant soles to protect against crushing injuries, slips, or falling objects in industrial settings.
- Respiratory Protection: Use respirators or masks when working in environments with dust, gases, vapors, or airborne contaminants. Ensure they are suitable for the specific hazards present.
- Head Protection: Wear hard hats or helmets to protect against head injuries from falling objects or impacts in industrial settings.
- Ear Protection: Use earplugs or earmuffs to safeguard against excessive noise levels often present in industrial environments where pressure sensors might be installed.
- Full-Body Suits/Apron: In situations involving exposure to hazardous chemicals or substances, full-body suits or aprons provide additional protection against splashes or spills.
The selection of PPE should align with the specific hazards present in the working environment and comply with industry regulations and safety standards. Proper training on the use, maintenance, and limitations of PPE is crucial to ensure its effectiveness in safeguarding against potential risks while working with pressure sensors.
How can classify PPE based on the level of hazard and risk assessment?
Classifying Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) based on the level of hazard and risk assessment involves categorizing PPE according to the specific risks present in the working environment. This classification is crucial for selecting the appropriate level of protection for personnel. Here's a general guideline for classifying PPE based on hazard levels:
- Examples: Minor mechanical risks, minimal exposure to chemicals, low noise levels.
- PPE Examples: Safety glasses, gloves, basic head protection (bump caps), earplugs.
- Examples: Moderate exposure to chemicals, machinery operations, and moderate noise levels.
- PPE Examples: Chemical-resistant gloves, safety helmets/hard hats, respirators, earmuffs.
- Examples: High-risk chemical exposure, heavy machinery operations, high noise levels, risk of fire or burns.
- PPE Examples: Full-body suits, flame-resistant clothing, chemical-resistant suits, face shields, and self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA).
- Examples: Specific hazards such as electrical work, radiation, and biological hazards.
- PPE Examples: Insulated gloves, electrical safety gear, radiation shields, biohazard suits.
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a thorough risk assessment of the workplace to identify potential hazards and assess their severity and likelihood of occurrence.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards that prescribe the required PPE based on the identified hazards.
- Manufacturer Recommendations: Follow manufacturer guidelines and specifications for PPE selection, considering the compatibility of the equipment with the hazards present.
- Training and Education: Provide adequate training to personnel on the proper use, maintenance, limitations, and disposal of PPE specific to the identified hazards.
By classifying PPE based on hazard levels and conducting comprehensive risk assessments, organizations can effectively select and provide the necessary protective gear to mitigate risks and ensure the safety of workers in diverse working environments.
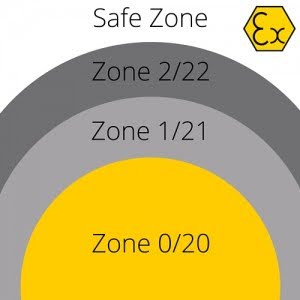
Fig 4. Hazardous zone
What are the Training and awareness programs for personnel safety?
Training and awareness programs for personnel safety are crucial in promoting a safety culture, equipping employees with the knowledge and skills to identify and mitigate risks, and fostering a safe working environment. Here are key elements and topics to include in such programs:
- Safety Procedures and Protocols: Train employees on company-specific safety procedures, including emergency response protocols, reporting procedures for incidents/near misses, and the use of safety equipment.
- Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment: Educate personnel on identifying workplace hazards, conducting risk assessments, and implementing controls to minimize risks, especially in hazardous areas.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Provide comprehensive training on the proper selection, use, maintenance, and limitations of PPE specific to their roles and potential hazards they might encounter.
- Equipment Operation and Maintenance: Train employees on the correct operation, handling, and maintenance of equipment, including pressure sensors, by manufacturer guidelines and safety protocols.
- Safe Work Practices: Educate personnel on safe work practices, such as proper lifting techniques, electrical safety, lockout/tagout procedures, and safe material handling.
- Chemical Handling and Hazardous Substances: Provide training on the safe handling, storage, and disposal of hazardous substances, including understanding Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and chemical labeling.
- Fire Safety and Emergency Procedures: Conduct training on fire prevention, evacuation procedures, and the use of fire extinguishers. Include drills to ensure employees are familiar with emergency routes and procedures.
- Health and Wellness: Promote awareness of health-related issues in the workplace, including ergonomics, stress management, and the importance of regular health check-ups.
- Behavioral Safety: Encourage a safety-conscious culture by addressing behavioral aspects, emphasizing the importance of reporting hazards, and near misses, and fostering a proactive safety mindset.
- Compliance with Regulations and Standards: Ensure employees understand and comply with relevant industry standards, local regulations, and best practices about safety in their specific work environment.
- Continuous Improvement: Promote a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging feedback, conducting safety audits, and implementing corrective actions based on findings.
- Supervisor and Leadership Training: Provide training to supervisors and leaders to effectively communicate safety expectations, lead by example, and support a positive safety culture.
Regular training sessions, refresher courses, toolbox talks, and incorporating safety discussions in daily operations help reinforce safety practices and contribute to a safer workplace environment. Encouraging active participation, feedback, and open communication channels further strengthen the effectiveness of these programs.
What are the Safety Audits and Assessments?
Safety audits and assessments are systematic evaluations conducted to identify potential hazards, assess compliance with safety regulations, and evaluate the effectiveness of safety measures in a workplace. These assessments help organizations maintain a safe working environment and prevent accidents. Here are key aspects of safety audits and assessments:
- Comprehensive Inspections: Safety audits involve thorough inspections of the workplace, equipment, processes, and safety protocols. They identify hazards, potential risks, and areas where safety measures might be inadequate.
- Regulatory Compliance: Assessments ensure compliance with local, national, and industry-specific safety regulations and standards. This includes verifying adherence to OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), ATEX, IECEx, NFPA (National Fire Protection Association), and other relevant guidelines.
- Risk Identification and Assessment: Evaluate the level of risk associated with various tasks, equipment, and working conditions. This involves identifying potential hazards, assessing their severity, and determining the likelihood of occurrence.
- Documentation Review: Review safety documentation, including safety policies, procedures, training records, incident reports, and maintenance logs. Ensure that documentation is up-to-date and in compliance with regulations.
- Observations and Interviews: Engage with employees at various levels through interviews and observations to assess their understanding of safety procedures, identify any gaps in knowledge or implementation, and gather feedback on safety measures.
- Safety Culture Assessment: Evaluate the organization's safety culture by examining attitudes, behaviors, and practices related to safety. Assess the level of commitment to safety among employees and management.
- Emergency Preparedness: Assess emergency response plans, evacuation procedures, and the availability and condition of safety equipment like fire extinguishers, first aid kits, and emergency exits.
- Corrective Action Planning: Identify deficiencies and non-compliance issues and develop a corrective action plan. Prioritize actions based on the severity of risks and timelines for implementation.
- Follow-up and Continuous Improvement: Conduct follow-up assessments to track the progress of corrective actions and ensure their effectiveness. Continuously review and improve safety protocols based on audit findings.
- Management Review: Present audit findings and recommendations to management for review and action. Management commitment and support are crucial for implementing necessary changes and fostering a culture of safety.
Safety audits and assessments are essential tools for identifying potential hazards, ensuring regulatory compliance, improving safety protocols, and creating a safer work environment. Regular audits, coupled with effective corrective actions and continuous improvement efforts, contribute significantly to enhancing workplace safety.

Fig 5. Ex-proof non-sparking differential pressure sensor
How can Conduct safety audits and assessments of pressure transmitter installations?
Conducting safety audits and assessments of pressure transmitter installations involves a systematic evaluation to ensure compliance with safety standards, identify potential hazards, and assess the effectiveness of safety measures in place. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Define the scope and objectives of the safety audit, specifying the areas, installations, or equipment to be assessed.
- Gather documentation related to pressure transmitter installations, including design specifications, installation records, maintenance logs, and safety procedures.
- Conduct a thorough inspection of pressure transmitter installations. Identify potential hazards such as electrical risks, incorrect wiring, inadequate grounding, or exposure to flammable substances.
- Assess the location, environment, and surrounding conditions for potential risks.
- Evaluate compliance with safety standards and regulations applicable to pressure transmitter installations in hazardous areas.
- Verify that the installations adhere to manufacturer guidelines and specifications for hazardous environments.
- Assess the level of risk associated with each installation, considering factors like the classification of hazardous zones, potential ignition sources, and the likelihood of exposure to flammable substances.
- Prioritize risks based on their severity and potential impact.
- Test the functionality and operation of pressure transmitters to ensure they are functioning correctly and providing accurate readings.
- Verify that safety features and alarms are operational and respond as intended.
- Document findings, including identified hazards, compliance status, and recommendations for improvement.
- Develop an action plan outlining corrective measures, timelines, responsible parties, and priorities based on the identified risks.
- Monitor the implementation of corrective actions and conduct follow-up audits to ensure their effectiveness.
- Continuously review and improve safety protocols based on audit findings and changes in regulations or industry standards.
How can Compliance check for safety regulations and standards?
Compliance checks for safety regulations and standards involve a systematic process to ensure that workplaces, equipment, procedures, and practices adhere to relevant safety regulations and industry standards. Here's a guide on conducting compliance checks:
Check for proper signage, labeling, emergency exits, fire safety measures, PPE availability, and equipment certifications.
Maintain comprehensive records of compliance checks, audits, corrective actions, and follow-up activities.
Regular compliance checks are essential to ensure ongoing adherence to safety regulations and standards, mitigate risks, and maintain a safe and healthy work environment.
Fig 6. Different location that pressure sensor can be installed
How can improve the safety practices of pressure sensors?
Improving the safety practices related to pressure sensors involves a comprehensive approach that addresses various aspects of their use, installation, maintenance, and surrounding operational environment. Here are several strategies to enhance safety practices:
By implementing these strategies, organizations can significantly improve the safety practices associated with pressure sensors, reduce risks, and create a safer working environment in hazardous areas.
Conclusion
Improving safety practices surrounding pressure sensors, especially in hazardous environments, is critical for ensuring a secure working environment and minimizing potential risks. By following comprehensive strategies that encompass training, compliance, proper installation and maintenance, protective measures, and a continuous improvement mindset, organizations can significantly enhance safety standards related to pressure sensors. Adhering to industry-specific regulations, conducting thorough risk assessments, and fostering a safety-conscious culture are integral elements in creating an environment where the use of pressure sensors is both efficient and safe. Continuous vigilance, regular inspections, and proactive measures contribute to sustaining safety levels, mitigating risks, and fostering a workplace where personnel feel confident in their operations while ensuring the integrity and reliability of pressure sensor systems.
To recap
Q: Are pressure sensors safe to use in hazardous environments?
A: Pressure sensors designed for hazardous areas adhere to specific safety standards (ATEX, IECEx, etc.) to minimize risks associated with potential ignition sources.
Q: What safety certifications should pressure sensors have for hazardous areas?
A: Certifications like ATEX and IECEx indicate compliance with safety standards for use in potentially explosive atmospheres.
Q: What are the risks associated with pressure sensor installations in hazardous locations?
A: Risks include potential ignition due to electrical faults, exposure to flammable substances, improper wiring, or inadequate grounding.
Q: How can I ensure the proper installation of pressure sensors in hazardous areas?
A: Follow manufacturer guidelines, ensure compliance with safety standards, use certified equipment, and conduct thorough inspections.
Q: What protective measures should be taken when working with pressure sensors in hazardous environments?
A: Employ intrinsically safe equipment, implement proper wiring and grounding, use protective enclosures, and provide adequate personnel training.
Q: What safety protocols should be in place for pressure sensor maintenance? A: Safety protocols should include isolation procedures, the use of intrinsically safe tools, proper PPE, and adherence to lockout/tagout practices.
Q: What should I consider when selecting Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for pressure sensor handling?
A: Choose PPE based on the specific hazards present, including safety glasses, gloves, flame-resistant clothing, and appropriate footwear.
Q: How often should pressure sensors in hazardous areas be inspected?
A: Conduct regular inspections based on manufacturer recommendations, regulatory requirements, and risk assessments, ensuring proper functionality and safety.
Q: What actions should be taken in case of a pressure sensor malfunction in a hazardous area?
A: Isolate the equipment, follow emergency procedures, inform relevant personnel, and initiate corrective actions as per safety protocols.
Q: How can I ensure compliance with safety regulations when using pressure sensors?
A: Regularly conduct safety audits, assess risks, maintain proper documentation, and train personnel to adhere to safety procedures and standards.
Q: Are there specific guidelines for pressure sensor installations in different hazardous zones?
A: Yes, zones are classified based on the likelihood of a potentially explosive atmosphere. Installations must comply with zone-specific safety requirements.
Q: What are the best practices for grounding pressure sensors in hazardous areas?
A: Properly bond and ground sensors using suitable methods and materials to prevent electrical hazards and mitigate the risk of sparking.
Q: What measures can improve the overall safety culture when working with pressure sensors?
A: Foster a safety-conscious environment through regular training, open communication, encouraging feedback, and implementing continuous improvement initiatives.
Q: How can I assess if pressure sensor installations meet safety standards and guidelines?
A: Conduct comprehensive assessments, review compliance with regulations, perform risk evaluations, and ensure adherence to manufacturer specifications.
Q: What steps should be taken to ensure ongoing safety with pressure sensor installations?
A: Regularly review and update safety protocols, conduct frequent inspections, provide continuous training, and stay informed about evolving safety standards.
References
https://www.heatingandprocess.com/product/process-instrumentation/process-pressure-measurement/
https://www.hitma-instrumentatie.nl/en/products/dwyer-atex-differential-pressure-switch-series-h3
https://www.turck.de/en/quick-disconnect-wiring-in-hazardous-area-642.php
+
Recent Posts
-
Mastering Water Pump Care in Dubai: Installation, Maintenance, Repair, and Efficiency Tips
I. IntroductionWhy Water Pumps Matter for Dubai HomesIn Dubai’s arid environment, water pumps are es …21st Nov 2024 -
How to Choose and Purchase the Right Water Pump in 2025: A Complete Guide for Dubai Homes
1. IntroductionIn 2025, water pumps have become an integral part of many homes in Dubai, ensuring a …14th Nov 2024 -
Damping the Chaos: The Role of a Pressure Snubber
Imagine this: A critical process is underway. A team of engineers has meticulously planned and …5th Nov 2024




